C#调用非托管DLL从零深入讲解
一、结构对齐
结构对齐是C#调用非托管DLL的必备知识。
在没有#pragma pack声明下结构体内存对齐的规则为:
- 第一个成员的偏移量为0,
- 每个成员的首地址为自身大小的整数倍
- 子结构体的第一个成员偏移量应当是子结构体最大成员的整数倍
- 结构体总大小必须是内部最大成员的整数倍
案例1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| struct TestFrame
{
unsigned char id;
int width;
long long height;
unsigned char* data;
};
|
案例2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| struct TestInfo
{
char username[10];
double userdata;
};
struct TestFrame
{
unsigned char id;
int width;
long long height;
unsigned char* data;
char mata;
TestInfo info;
};
|
查看具体的地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
#define FIELDOFFSET(TYPE,MEMBER) (int)(&(((TYPE*)0)->MEMBER))
int infoLen = sizeof(TestInfo);
int offsetusername = FIELDOFFSET(TestInfo, username);
int offsetuserdata = FIELDOFFSET(TestInfo, userdata);
|
使用#pragma pack 这个宏声明按照几个字节对齐
1
2
3
4
5
6
| #pragma pack(1)
struct TestInfo
{
char username[10];
double userdata;
};
|
如果我设置#pragma pack(10)则结果
1
2
3
4
5
| struct TestInfo
{
char username[10];
double userdata;
};
|
这与不使用#pragma pack(10)结果相同,也就是说是按照宏声明的和实际数据类型中最大值中的较小的那个来决定
在C#中自定义结构对齐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential,Pack =1)]
public struct TestFrame
{
public char id;
int width;
long height;
char mata;
};
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)]
public struct TestFrame
{
[FieldOffset(0)]
public char id;
[FieldOffset(10)]
int width;
[FieldOffset(15)]
long height;
[FieldOffset(40)]
char mata;
};
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.BStr)]
public string name;
|
二、调用约定
经常用到的调用约定有两种,C语言调用约定(_cdecl)和标准调用约定(_stdcall)。两种方式都是按照从右至左的方式入栈,但是C语言调用约定函数本身不清理栈,此工作由调用者负责,所以允许可变参数。而标准调用约定则是函数本身调用栈。
c语言调用约定和标准调用约定的最大区别在于,谁来清理参数所在的栈,C则调用者来清理,标准则是函数本身来清理。当所调用的程序中有可变参数的函数时,建议采用C语言约定
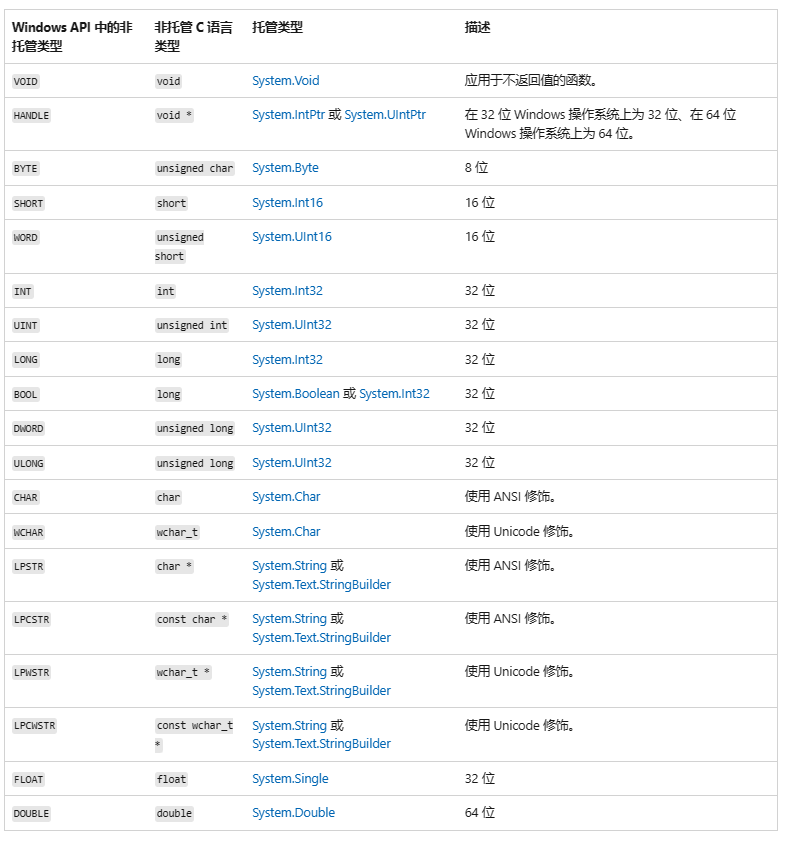
三、常用数据对应关系
常用的数据结构类型对比
| C# | C/C++ |
|---|
| sbyte/char | char |
| short | short |
| int | int |
| long | long long/int64_t |
| float | float |
| double | double |
| intPtr/[] | void * |
四、创建并调用dll
本章节使用C++创建一个dll库,并使用C#和C++来调用
- 新建一个dll链接库项目,删除所有文件,新增Native.h和Native.cpp
- 在Native.h中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| #pragma once
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define EXTERNC extern "C"
#else
#define EXTERNC
#endif
#ifdef DLL_IMPORT
#define HEAD EXTERNC __declspec(dllimport)
#else
#define HEAD EXTERNC __declspec(dllexport)
#endif
#define CallingConvention __cdecl
|
- 在Native.cpp中实现函数,并编译为DLL路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include "Native.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<Windows.h>
HEAD void CallingConvention Test1()
{
printf("调用成功\n");
}
|
在C#中调用
一定要设置好对应的NativeDll.dll路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll")]
public static extern void Test1();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1();
}
|
在C++中调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #include <iostream>
#include <stdarg.h>
#define DLL_IMPORT
#include "../NativeDll/Native.h"
#pragma comment(lib,"../bin/NativeDll.lib")
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
Test1();
}
|
五、DllImpoert常用参数
DllImport常见参数有:
dllName:动态链接库的名称,必填
引用路径: (1)exe运行程序所在的目录
(2)System32目录
(3)环境变量目录
(4)自定义路径,如:DllImport(@”C:\OJ\Bin\Judge.dll”)
CallingConvention:调用约定,常用的为Cdecl和StdCall,默认约定为StdCall
CharSet:设置字符串编码格式
EntryPoint:函数入口名称,默认使用方法本身的名字
ExactSpelling:是否必须与入口点的拼写完全匹配,默认为true,如果为false,则根据CharSet来找函数的A版本还是W版本。
这是一个CreateWindow的定义,后面有两个版本W和A。
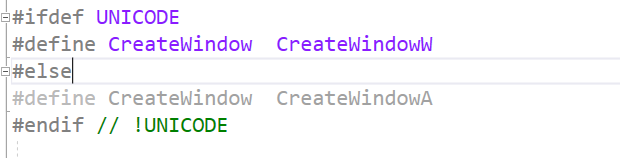
ExactSpelling,如果为true则只会使用CreateWindow,如果为False,则会选择W或者A版本,会自动根据当前系统采用的是那种UNICODE选择
SetLastError:指示方法是否保留Win32的上一个错误,默认false。如果为true,则使用Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()来获取错误码。
六、基本数据传递和函数返回值
基本数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
|
HEAD void CallingConvention TestBasicData(char d1, short d2, int d3, long long d4, float d5, double d6)
{
printf("d1:%d,d2:%d,d3:%d,d4:%lld,d5:%f,d6:%lf\n", d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestBasicData(
char d1,
short d2,
int d3,
long d4,
float d5,
double d6
);
|
按引用传递基本数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestBasicDataRef(char& d1, short& d2, int& d3, long long& d4, float& d5, double& d6)
{
d1 = 1;
d2 = 2;
d3 = 3;
d4 = 4;
d5 = 5.6f;
d6 = 6.7;
printf("d1:%d,d2:%d,d3:%d,d4:%lld,d5:%f,d6:%lf\n", d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestBasicDataRef(
ref char d1,
ref short d2,
ref int d3,
ref long d4,
ref float d5,
ref double d6
);
char a1 ='a'; short a2 = 3; int a3 = 33; long a4 = 3333;float a5 = 333.33f; double a6 = 333.3333d;
TestBasicDataRef(ref a1, ref a2,ref a3,ref a4,ref a5,ref a6);
|
按引用传递可以在被调用中更改参数值
使用指针传递值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestBasicDataPointer(char* d1, short* d2, int* d3, long long* d4, float* d5, double* d6)
{
*d1 = 10;
*d2 = 20;
*d3 = 30;
*d4 = 40;
*d5 = 50.6f;
*d6 = 60.7;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestBasicDataPointer(
ref char d1,
ref short d2,
ref int d3,
ref long d4,
ref float d5,
ref double d6
);
char a1 ='a'; short a2 = 3; int a3 = 33; long a4 = 3333;float a5 = 333.33f; double a6 = 333.3333d;
TestBasicDataPointer(ref a1, ref a2, ref a3, ref a4, ref a5, ref a6);
|
调用带返回值的方法
1
2
3
4
| HEAD float CallingConvention TestAdd(float num1, float num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern float TestAdd(float num1, float num2);
var sum=TestAdd(3.4f,3.3f);
|
七、数组的传递与传出
直接使用数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestBsicArr(int arr1[], float arr2[])
{
int tmp1[3];
float tmp2[3];
memcpy(tmp1, arr1, sizeof(tmp1));
memcpy(tmp2, arr2, sizeof(tmp2));
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern float TestBsicArr(int[] num1, float[] num2);
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3 };
float[] arr2 = { 11.2f,33f,3.3f};
TestBsicArr(arr1, arr2);
|
使用指针
不建议使用上面的方式,建议使用指针来替代数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestBsicArrPointer(int* arr1, float* arr2)
{
int tmp1[3];
float tmp2[3];
memcpy(tmp1, arr1, sizeof(tmp1));
memcpy(tmp2, arr2, sizeof(tmp2));
arr1[0] = 100;
arr2[2] = 8888.55555f;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern float TestBsicArrPointer(int[] num1, float[] num2);
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2, 3 };
float[] arr2 = { 11.2f,33f,3.3f};
TestBsicArrPointer(arr1,arr2);
|
返回数组
1
2
3
4
5
| int arr[3] = { 1,2,3 };
HEAD void* CallingConvention TestBsicArrReturn()
{
return arr;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr TestBsicArrReturn();
IntPtr arr = TestBsicArrReturn();
int[] returnArr = new int[3];
Marshal.Copy(arr, returnArr, 0, 3);
|
八、传递字符串
直接传递字符串
1
2
3
4
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestString(char* str)
{
printf("str:%s\n", str);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestString(string str);
TestString("你好");
|
使用byte传递字符串
1
2
3
4
| HEAD void CallingConvention TestStringByte(char* str)
{
printf("str:%s\n", str);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestStringByte(byte[] str);
var arr1 = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("hello");
TestStringByte(arr1.Concat(new byte[1] { 0 }).ToArray());
|
九、结构体的传入与传出
结构体作为参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
struct ChildStruct
{
int num;
double pi;
};
struct StructA
{
short id;
ChildStruct cs;
};
HEAD void CallingConvention TestStruct(StructA* param)
{
param->id = 3;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestStruct(ref StructA param);
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct ChildStruct
{
public int num;
public double pi;
};
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct StructA
{
public short id;
public ChildStruct cs;
};
StructA testStruct = new StructA();
testStruct.id = 2;
testStruct.cs.num = 1000;
testStruct.cs.pi = 3.1415d;
TestStruct(ref testStruct);
|
结构体中有数组和其他结构体指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| struct ChildStruct
{
int num;
double pi;
};
struct StructB
{
short id;
ChildStruct cs;
ChildStruct* pcs;
int nums[5];
};
HEAD void CallingConvention TestStructB(StructB* param)
{
param->id = 3;
}
HEAD void* CallingConvention ConvertChildStruct(ChildStruct* cs)
{
return cs;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void TestStructB(ref StructB param);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr ConvertChildStruct(ref ChildStruct param);
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct ChildStruct
{
public int num;
public double pi;
};
public struct StructB
{
public short id;
public ChildStruct cs;
public IntPtr pcs;
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValArray,SizeConst =5)]
public int[] nums;
};
StructB testStructB = new StructB();
testStructB.id = 2;
testStructB.cs.num = 1000;
ChildStruct cs = new ChildStruct();
cs.num = 100;
testStructB.nums = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
testStructB.nums[i] = i;
}
testStructB.pcs = ConvertChildStruct(ref cs);
TestStructB(ref testStructB);
|
返回结构体-先声明结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
struct ChildStruct
{
int num;
double pi;
};
struct StructA
{
short id;
ChildStruct cs;
};
StructA structa;
HEAD void* CallingConvention TestStructReturn()
{
structa.id = 1222;
structa.cs.num = 100;
structa.cs.pi = 66666;
return &structa;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr TestStructReturn();
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct ChildStruct
{
public int num;
public double pi;
};
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct StructA
{
public short id;
public ChildStruct cs;
};
IntPtr ptr = TestStructReturn();
StructA structA = Marshal.PtrToStructure<StructA>(ptr);
|
返回结构体-不用声明结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| struct FrameInfo
{
char username[20];
double pts;
};
struct Frame
{
int width;
int height;
int format;
int lineSize[4];
unsigned char* data[4];
FrameInfo* info;
};
Frame frame;
FrameInfo info;
HEAD void* CallingConvention TestComplexStructReturn()
{
frame.width = 1920;
frame.height = 1080;
frame.format = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
frame.lineSize[i] = 100 * i;
frame.data[i] = new unsigned char[10];
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
frame.data[i][j] = i;
}
}
info.pts = 333.44;
memset(info.username, 0, 20);
memcpy(info.username, "hello,world", strlen("hello,world"));
frame.info = &info;
return &frame;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr TestComplexStructReturn();
IntPtr ptr = TestComplexStructReturn();
int width= Marshal.ReadInt32(ptr, 0);
int height = Marshal.ReadInt32(ptr,4);
int format = Marshal.ReadInt32(ptr, 8);
int[] linesize = new int[4];
Marshal.Copy(new IntPtr(ptr.ToInt64()+12), linesize, 0, 4);
IntPtr[] datas = new IntPtr[4];
Marshal.Copy(new IntPtr(ptr.ToInt64() + 32), datas, 0, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
byte[] tmp = new byte[10];
Marshal.Copy(datas[i], tmp, 0, 10);
}
IntPtr infoPtr = Marshal.ReadIntPtr(ptr, 64);
byte[] username = new byte[20];
Marshal.Copy(infoPtr, username, 0, 20);
string str = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(username);
double pts = BitConverter.ToDouble(BitConverter.GetBytes(Marshal.ReadInt64(infoPtr, 24)), 0);
|
十、传递可变参数
可变参数需要使用C语言调用约定,如果不涉及可变参数,则可以使用标准调用约定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| HEAD float CallingConvention TestSum(int length, ...)
{
char* head = (char*)&length;
int num1 = *(long long*)(head + 8);
int num2 = *(long long*)(head + 16);
int num3 = *(long long*)(head + 24);
int num4 = *(long long*)(head + 32);
double num5 = *(double*)(head + 40);
return num1 + num2 + num3 + num4 + num5;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| [DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern float TestSum(int length,__arglist);
float sum = TestSum(5, __arglist(1, 2, 3, 4,33.33d));
|
十一、C++回调C#中的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef int (*pfun)(int level, void* ptr);
HEAD void CallingConvention SetLogFuncPointer(pfun p)
{
int ret = p(0, NULL);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
[UnmanagedFunctionPointer(CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public delegate int Log(int level, IntPtr ptr);
public static Log LogFuncptr = LogCllBack;
static int LogCllBack(int level,IntPtr ptr)
{
return 0;
}
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void SetLogFuncPointer(Log logptr);
SetLogFuncPointer(LogFuncptr);
|
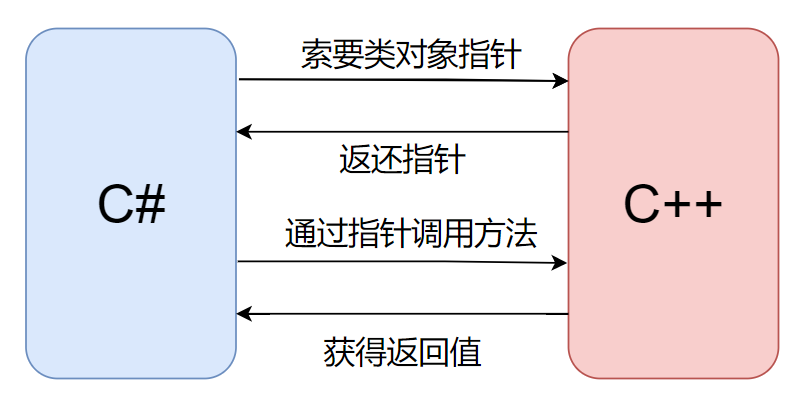
十二、传递类对象
如何将类的数据进行传输——答案是不可能。
C#其实不能创建非托管类的实例,也不能销毁。非托管内存分配器、构造函数、析构函数等都是由C++编译器来实现的,如果想要实现类的数据传输,则需要C++/CLR包装器。
但是可以使用类的指针实现类数据的传递。
- 在C++中声明类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
class WishList
{
public:
WishList(std::string name) :_name(name), _items(){};
std::string getName();
void setName(std::string name);
int countItems();
void addItem(std::string item);
void removeItem(std::string item);
void print();
private:
std::string _name;
std::vector<std::string> _items;
};
std::string WishList::getName()
{
return _name;
}
void WishList::setName(std::string name)
{
_name = name;
}
void WishList::addItem(std::string item)
{
_items.push_back(item);
}
void WishList::removeItem(std::string item)
{
for (int i = 0; i < _items.size(); ++i) {
if (_items[i] == item) {
_items.erase(_items.begin() + i);
}
}
}
int WishList::countItems() {
return _items.size();
}
void WishList::print() {
for (std::string item : _items) {
std::cout << item << std::endl;
}
}
|
- 声明类后,写一个类的wrapper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
HEAD WishList* CallingConvention CreateWishList(const char* name);
HEAD void CallingConvention DeleteWishList(WishList* wishList);
HEAD std::string CallingConvention GetWishListName(WishList* wishList);
HEAD void CallingConvention SetWishListName(WishList* wishList, const char* name);
HEAD void CallingConvention AddWishListItem(WishList* wishList, const char* name);
HEAD void CallingConvention RemoveWishListItem(WishList* wishList, const char* name);
HEAD int CallingConvention CountWishListItems(WishList* wishList);
HEAD void CallingConvention PrintWishList(WishList* wishList);
HEAD WishList* CallingConvention CreateWishList(const char* name)
{
return new WishList(name);
}
HEAD void CallingConvention DeleteWishList(WishList* wishList)
{
delete wishList;
}
HEAD std::string CallingConvention GetWishListName(WishList* wishList)
{
return wishList->getName();
}
HEAD void CallingConvention SetWishListName(WishList* wishList, const char* name)
{
wishList->setName(name);
}
HEAD void CallingConvention AddWishListItem(WishList* wishList, const char* name)
{
wishList->addItem(name);
}
HEAD void CallingConvention RemoveWishListItem(WishList* wishList, const char* name)
{
wishList->removeItem(name);
}
HEAD int CallingConvention CountWishListItems(WishList* wishList)
{
return wishList->countItems();
}
HEAD void CallingConvention PrintWishList(WishList* wishList)
{
wishList->print();
}
|
- 在C#中声明对应的类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| public class WishList
{
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern IntPtr CreateWishList(string name);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern void DeleteWishList(IntPtr wishListPointer);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.BStr)]
private static extern string GetWishListName(IntPtr wishListPointer);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern void SetWishListName(IntPtr wishListPointer, string name);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern void AddWishListItem(IntPtr wishListPointer, string name);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern void RemoveWishListItem(IntPtr wishListPointer, string name);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern int CountWishListItems(IntPtr wishListPointer);
[DllImport("../../NativeDll.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern void PrintWishList(IntPtr wishListPointer);
private readonly IntPtr _wishListPointer;
public WishList(string name)
{
_wishListPointer = CreateWishList(name);
}
~WishList()
{
DeleteWishList(_wishListPointer);
}
public string Name
{
get { return GetWishListName(_wishListPointer); }
set { SetWishListName(_wishListPointer, value); }
}
public int Count => CountWishListItems(_wishListPointer);
public void AddItem(string name)
{
AddWishListItem(_wishListPointer, name);
}
public void RemoveItem(string name)
{
RemoveWishListItem(_wishListPointer, name);
}
public void Print()
{
PrintWishList(_wishListPointer);
}
}
|
- 在C#中调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| WishList wishList = new WishList("我的愿望清单");
wishList.AddItem("iphone");
wishList.AddItem("ipad");
wishList.AddItem("macbook");
wishList.AddItem("work");
wishList.Print();
Console.WriteLine("=====================================");
wishList.RemoveItem("work");
wishList.Print();
|
实现结果:











