6、LLamaIndex简介
1、大语言模型开发框架的价值是什么?
SDK:Software Development Kit,它是一组软件工具和资源的集合,旨在帮助开发者创建、测试、部署和维护应用程序或软件。
所有开发框架(SDK)的核心价值,都是降低开发、维护成本。
大语言模型开发框架的价值,是让开发者可以更方便地开发基于大语言模型的应用。主要提供两类帮助:
- 第三方能力抽象。比如 LLM、向量数据库、搜索接口等
- 常用工具、方案封装
- 底层实现封装。比如流式接口、超时重连、异步与并行等
好的开发框架,需要具备以下特点:
- 可靠性、鲁棒性高
- 可维护性高
- 可扩展性高
- 学习成本低
举些通俗的例子:
- 与外部功能解依赖
- 比如可以随意更换 LLM 而不用大量重构代码
- 更换三方工具也同理
- 经常变的部分要在外部维护而不是放在代码里
- 比如 Prompt 模板
- 各种环境下都适用
- 比如线程安全
- 方便调试和测试
- 至少要能感觉到用了比不用方便吧
- 合法的输入不会引发框架内部的报错
🌰 举个例子:使用 SDK,4 行代码实现一个简易的 RAG 系统
1 | !pip install --upgrade llama-index |
1 | from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader |
1 | response = query_engine.query("llama2有多少参数") |
Llama 2 ranges in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
2、LlamaIndex 介绍
LlamaIndex 是一个为开发「上下文增强」的大语言模型应用的框架(也就是 SDK)。上下文增强,泛指任何在私有或特定领域数据基础上应用大语言模型的情况。例如:
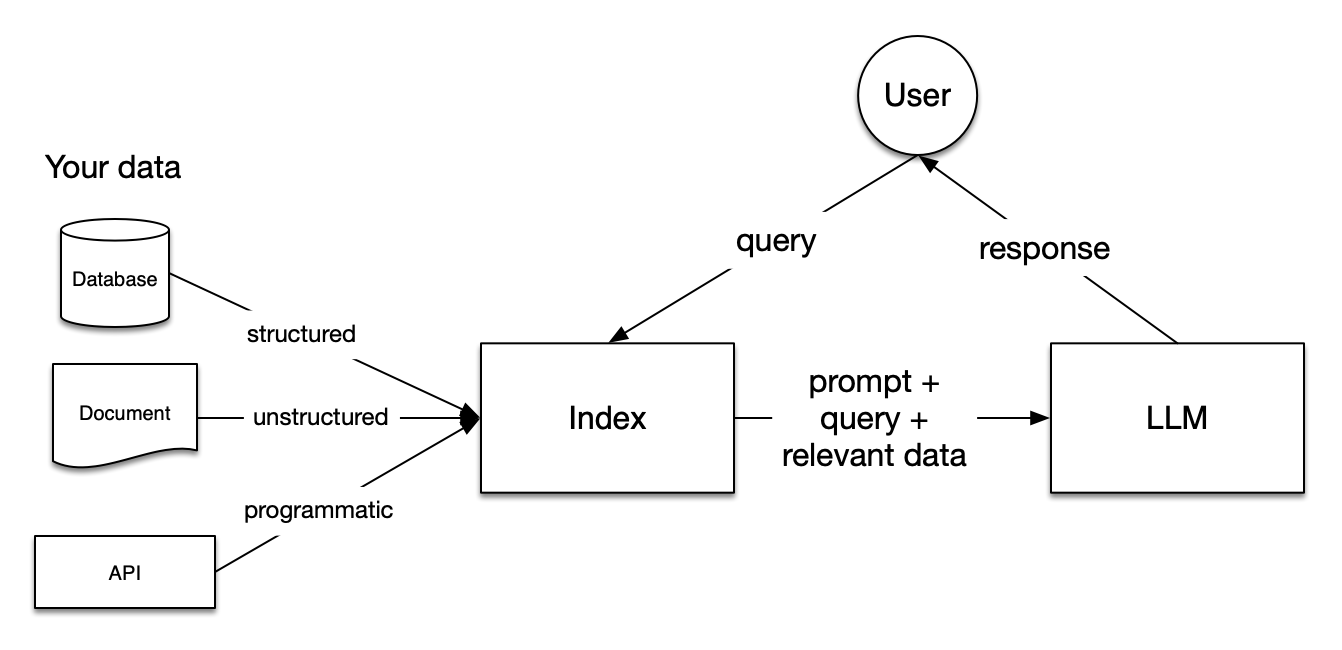
Question-Answering Chatbots (也就是 RAG)
Document Understanding and Extraction (文档理解与信息抽取)
Autonomous Agents that can perform research and take actions (智能体应用)
LlamaIndex 有 Python 和 Typescript 两个版本,Python 版的文档相对更完善。
Python 文档地址:https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/
Python API 接口文档:https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/api_reference/
TS 文档地址:https://ts.llamaindex.ai/
TS API 接口文档:https://ts.llamaindex.ai/api/
LlamaIndex 是一个开源框架,Github 链接:https://github.com/run-llama
LlamaIndex 的核心模块
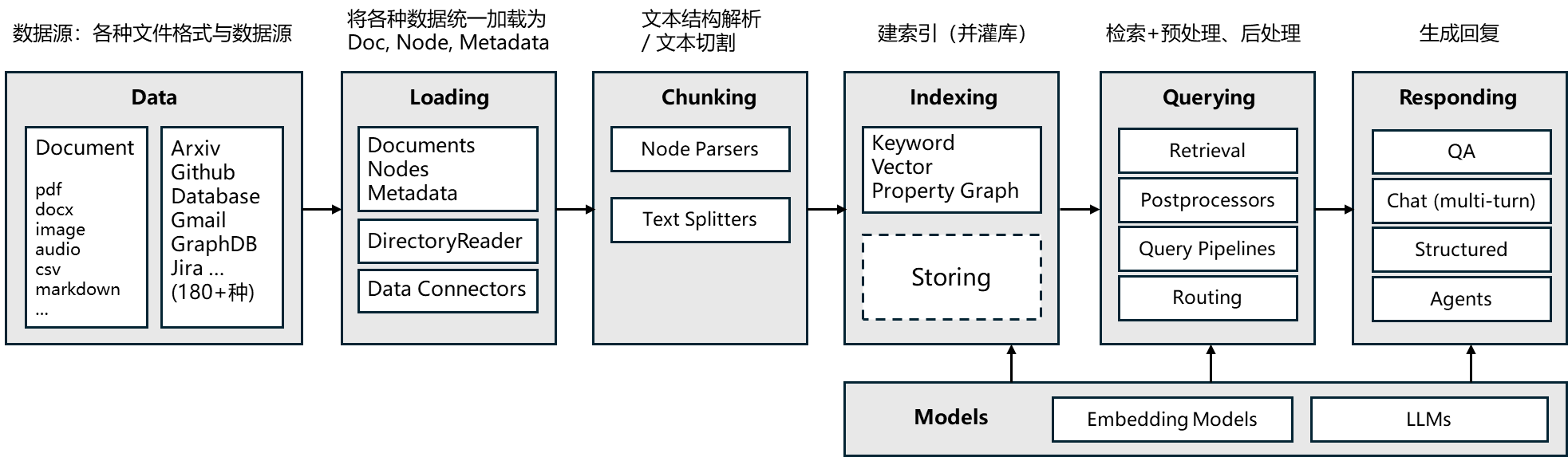
安装 LlamaIndex
- Python
1 | pip install llama-index |
- Typescript
1 | # 通过 npm 安装 |
本课程以 Python 版为例进行讲解。
3、数据加载(Loading)
3.1、加载本地数据
SimpleDirectoryReader 是一个简单的本地文件加载器。它会遍历指定目录,并根据文件扩展名自动加载文件(文本内容)。
支持的文件类型:
.csv- comma-separated values.docx- Microsoft Word.epub- EPUB ebook format.hwp- Hangul Word Processor.ipynb- Jupyter Notebook.jpeg,.jpg- JPEG image.mbox- MBOX email archive.md- Markdown.mp3,.mp4- audio and video.pdf- Portable Document Format.png- Portable Network Graphics.ppt,.pptm,.pptx- Microsoft PowerPoint
1 | import json |
1 | from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader |
1 | print(documents[0].text) |
Llama 2: OpenFoundation andFine-Tuned ChatModels
Hugo Touvron∗Louis Martin†Kevin Stone†
Peter Albert Amjad Almahairi Yasmine Babaei Nikolay Bashlykov SoumyaBatra
Prajjwal Bhargava Shruti Bhosale Dan Bikel LukasBlecher Cristian CantonFerrer MoyaChen
Guillem Cucurull David Esiobu Jude Fernandes Jeremy Fu Wenyin Fu BrianFuller
Cynthia Gao VedanujGoswami NamanGoyal AnthonyHartshorn Saghar Hosseini RuiHou
Hakan Inan Marcin Kardas Viktor Kerkez Madian Khabsa IsabelKloumann ArtemKorenev
Punit Singh Koura Marie-AnneLachaux ThibautLavril Jenya Lee Diana Liskovich
Yinghai Lu YuningMao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov PushkarMishra
Igor Molybog Yixin Nie AndrewPoulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi Rungta Kalyan Saladi
Alan Schelten Ruan Silva EricMichael Smith Ranjan Subramanian XiaoqingEllenTan BinhTang
Ross Taylor AdinaWilliams JianXiang Kuan PuxinXu ZhengYan Iliyan Zarov YuchenZhang
Angela Fan MelanieKambadur SharanNarang Aurelien Rodriguez RobertStojnic
Sergey Edunov ThomasScialom∗
GenAI, Meta
Abstract
In this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a collection of pretrained and fine-tuned
large language models (LLMs) ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
Our fine-tuned LLMs, called Llama 2-Chat , are optimized for dialogue use cases. Our
models outperform open-source chat models on most benchmarks we tested, and based on
ourhumanevaluationsforhelpfulnessandsafety,maybeasuitablesubstituteforclosed-
source models. We provide a detailed description of our approach to fine-tuning and safety
improvements of Llama 2-Chat in order to enable the community to build on our work and
contribute to the responsibledevelopmentof LLMs.
∗Equal contribution, corresponding authors: {tscialom, htouvron}@meta.com
†Second author
Contributions for all the authors can be found in Section A.1.arXiv:2307.09288v2 [cs.CL] 19 Jul 2023
{
"id_": "045248bf-9292-4c32-a82c-abfb63ca0aaa",
"embedding": null,
"metadata": {
"page_label": "1",
"file_name": "llama2-extracted.pdf",
"file_path": "/home/jovyan/lecture-notes/07-llamaindex/data/llama2-extracted.pdf",
"file_type": "application/pdf",
"file_size": 401338,
"creation_date": "2024-06-14",
"last_modified_date": "2024-06-14"
},
"excluded_embed_metadata_keys": [
"file_name",
"file_type",
"file_size",
"creation_date",
"last_modified_date",
"last_accessed_date"
],
"excluded_llm_metadata_keys": [
"file_name",
"file_type",
"file_size",
"creation_date",
"last_modified_date",
"last_accessed_date"
],
"relationships": {},
"text": "Llama 2: OpenFoundation andFine-Tuned ChatModels\nHugo Touvron∗Louis Martin†Kevin Stone†\nPeter Albert Amjad Almahairi Yasmine Babaei Nikolay Bashlykov SoumyaBatra\nPrajjwal Bhargava Shruti Bhosale Dan Bikel LukasBlecher Cristian CantonFerrer MoyaChen\nGuillem Cucurull David Esiobu Jude Fernandes Jeremy Fu Wenyin Fu BrianFuller\nCynthia Gao VedanujGoswami NamanGoyal AnthonyHartshorn Saghar Hosseini RuiHou\nHakan Inan Marcin Kardas Viktor Kerkez Madian Khabsa IsabelKloumann ArtemKorenev\nPunit Singh Koura Marie-AnneLachaux ThibautLavril Jenya Lee Diana Liskovich\nYinghai Lu YuningMao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov PushkarMishra\nIgor Molybog Yixin Nie AndrewPoulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi Rungta Kalyan Saladi\nAlan Schelten Ruan Silva EricMichael Smith Ranjan Subramanian XiaoqingEllenTan BinhTang\nRoss Taylor AdinaWilliams JianXiang Kuan PuxinXu ZhengYan Iliyan Zarov YuchenZhang\nAngela Fan MelanieKambadur SharanNarang Aurelien Rodriguez RobertStojnic\nSergey Edunov ThomasScialom∗\nGenAI, Meta\nAbstract\nIn this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a collection of pretrained and fine-tuned\nlarge language models (LLMs) ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.\nOur fine-tuned LLMs, called Llama 2-Chat , are optimized for dialogue use cases. Our\nmodels outperform open-source chat models on most benchmarks we tested, and based on\nourhumanevaluationsforhelpfulnessandsafety,maybeasuitablesubstituteforclosed-\nsource models. We provide a detailed description of our approach to fine-tuning and safety\nimprovements of Llama 2-Chat in order to enable the community to build on our work and\ncontribute to the responsibledevelopmentof LLMs.\n∗Equal contribution, corresponding authors: {tscialom, htouvron}@meta.com\n†Second author\nContributions for all the authors can be found in Section A.1.arXiv:2307.09288v2 [cs.CL] 19 Jul 2023",
"mimetype": "text/plain",
"start_char_idx": null,
"end_char_idx": null,
"text_template": "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}",
"metadata_template": "{key}: {value}",
"metadata_seperator": "\n",
"class_name": "Document"
}
Data Connectors。默认的 PDFReader 效果并不理想,我们可以更换文件加载器
1 | # !pip install pymupdf |
1 | from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader |
Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models
Hugo Touvron∗
Louis Martin†
Kevin Stone†
Peter Albert Amjad Almahairi Yasmine Babaei Nikolay Bashlykov Soumya Batra
Prajjwal Bhargava Shruti Bhosale Dan Bikel Lukas Blecher Cristian Canton Ferrer Moya Chen
Guillem Cucurull David Esiobu Jude Fernandes Jeremy Fu Wenyin Fu Brian Fuller
Cynthia Gao Vedanuj Goswami Naman Goyal Anthony Hartshorn Saghar Hosseini Rui Hou
Hakan Inan Marcin Kardas Viktor Kerkez Madian Khabsa Isabel Kloumann Artem Korenev
Punit Singh Koura Marie-Anne Lachaux Thibaut Lavril Jenya Lee Diana Liskovich
Yinghai Lu Yuning Mao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov Pushkar Mishra
Igor Molybog Yixin Nie Andrew Poulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi Rungta Kalyan Saladi
Alan Schelten Ruan Silva Eric Michael Smith Ranjan Subramanian Xiaoqing Ellen Tan Binh Tang
Ross Taylor Adina Williams Jian Xiang Kuan Puxin Xu Zheng Yan Iliyan Zarov Yuchen Zhang
Angela Fan Melanie Kambadur Sharan Narang Aurelien Rodriguez Robert Stojnic
Sergey Edunov
Thomas Scialom∗
GenAI, Meta
Abstract
In this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a collection of pretrained and fine-tuned
large language models (LLMs) ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
Our fine-tuned LLMs, called Llama 2-Chat, are optimized for dialogue use cases. Our
models outperform open-source chat models on most benchmarks we tested, and based on
our human evaluations for helpfulness and safety, may be a suitable substitute for closed-
source models. We provide a detailed description of our approach to fine-tuning and safety
improvements of Llama 2-Chat in order to enable the community to build on our work and
contribute to the responsible development of LLMs.
∗Equal contribution, corresponding authors: {tscialom, htouvron}@meta.com
†Second author
Contributions for all the authors can be found in Section A.1.
arXiv:2307.09288v2 [cs.CL] 19 Jul 2023
更多的 PDF 加载器还有 SmartPDFLoader 和 LlamaParse, 二者都提供了更丰富的解析能力,包括解析章节与段落结构等。但不是 100%准确,偶有文字丢失或错位情况,建议根据自身需求详细测试评估。
3.2、Data Connectors
用于处理更丰富的数据类型,并将其读取为 Document 的形式(text + metadata)。
例如:加载一个飞书文档。(飞书文档 API 访问权限申请,请参考此说明文档)
1 | # !pip install llama-index-readers-feishu-docs |
1 | from llama_index.readers.feishu_docs import FeishuDocsReader |
AI 大模型全栈工程师培养计划 - AGIClass.ai
由 AGI 课堂推出的社群型会员制课程,传授大模型的原理、应用开发技术和行业认知,助你成为 ChatGPT 浪潮中的超级个体
什么是 AI 大模型全栈工程师?
「AI 大模型全栈工程师」简称「AI 全栈」,是一个人就能借助 AI,设计、开发和运营基于 AI 的大模型应用的超级个体。
AI 全栈需要懂业务、懂 AI、懂编程,一个人就是一个团队,单枪匹马创造财富。
在技术型公司,AI 全栈最懂 AI,瞬间站上技术顶峰。
在非技术型公司,AI 全栈连接其他员工和 AI,提升整个公司的效率。
在公司外,AI 全栈接项目,独立开发变现小工具,赚取丰厚副业收入。
适合人群
学习本课程,可以在下述目标中三选一:
成为 AI 全栈:懂业务、懂 AI 也懂编程。大量使用 AI,自己完成 AI 应用从策划、开发到落地的全过程。包括商业分析、需求分析、产品设计、开发、测试、市场推广和运营等
成为业务向 AI 全栈:懂业务也懂 AI,与程序员合作,一起完成 AI 应用从策划、开发到落地的全过程
成为编程向 AI 全栈:懂编程也懂 AI,与业务人员合作,一起完成 AI 应用从策划、开发到落地的全过程
懂至少一门编程语言,并有过真实项目开发经验的软件开发⼯程师、⾼级⼯程师、技术总监、研发经理、架构师、测试⼯程师、数据工程师、运维工程师等,建议以「AI 全栈」为目标。即便对商业、产品、市场等的学习达不到最佳,但已掌握的经验和认知也有助于成为有竞争力的「编程向AI 全栈」。
不懂编程的产品经理、需求分析师、创业者、老板、解决方案工程师、项目经理、运营、市场、销售、设计师等,建议优先选择「业务向 AI 全栈」为目标。在课程提供的技术环境里熏陶,提高技术领域的判断力,未来可以和技术人员更流畅地沟通协作。学习过程中,如果能善用 AI 学习编程、辅助编程,就可以向「AI 全栈」迈进。
师资力量
首席讲师 - 王卓然
image.png
哈尔滨工业大学本硕,英国 UCL 博士,国际知名学者、企业家,师从统计机器学习理论奠基人之一 John Shawe-Taylor 教授,是最早从事人机对话研究的华裔学者之一,至今已超 20 年。
他就是 AI 全栈,仍在研发一线,单人销售、售前、开发、实施全流程交付多个数百万金额 AI 项目,全栈实战经验
4、文本切分与解析(Chunking)
为方便检索,我们通常把 Document 切分为 Node。
在 LlamaIndex 中,Node 被定义为一个文本的「chunk」。
4.1、使用 TextSplitters 对文本做切分
例如:TokenTextSplitter 按指定 token 数切分文本
1 | from llama_index.core import Document |
1 | show_json(nodes[0].json()) |
{
"id_": "0a1eee9a-635a-4391-8b74-75bf3c648f0e",
"embedding": null,
"metadata": {
"document_id": "FULadzkWmovlfkxSgLPcE4oWnPf"
},
"excluded_embed_metadata_keys": [],
"excluded_llm_metadata_keys": [],
"relationships": {
"1": {
"node_id": "9cd5baeb-1c59-448a-9c95-df7fb634b6bb",
"node_type": "4",
"metadata": {
"document_id": "FULadzkWmovlfkxSgLPcE4oWnPf"
},
"hash": "aa5f32dabade1da0e01c23cb16e160b624565d09a4a2a07fb7f7fd4d45aac88a",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"3": {
"node_id": "1a1aa20f-a88a-49a6-a0c6-fd13700022e4",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {},
"hash": "654c6cbdd5a23946a84e84e6f3a474de2a442191b2be2d817ba7f04286b1a980",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
}
},
"text": "AI 大模型全栈工程师培养计划 - AGIClass.ai\n\n由 AGI 课堂推出的社群型会员制课程,传授大模型的原理、应用开发技术和行业认知,助你成为",
"mimetype": "text/plain",
"start_char_idx": 0,
"end_char_idx": 76,
"text_template": "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}",
"metadata_template": "{key}: {value}",
"metadata_seperator": "\n",
"class_name": "TextNode"
}
{
"id_": "1a1aa20f-a88a-49a6-a0c6-fd13700022e4",
"embedding": null,
"metadata": {
"document_id": "FULadzkWmovlfkxSgLPcE4oWnPf"
},
"excluded_embed_metadata_keys": [],
"excluded_llm_metadata_keys": [],
"relationships": {
"1": {
"node_id": "9cd5baeb-1c59-448a-9c95-df7fb634b6bb",
"node_type": "4",
"metadata": {
"document_id": "FULadzkWmovlfkxSgLPcE4oWnPf"
},
"hash": "aa5f32dabade1da0e01c23cb16e160b624565d09a4a2a07fb7f7fd4d45aac88a",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"2": {
"node_id": "0a1eee9a-635a-4391-8b74-75bf3c648f0e",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {
"document_id": "FULadzkWmovlfkxSgLPcE4oWnPf"
},
"hash": "b08e60a1cf7fa55aa8c010d792766208dcbb34e58aeead16dca005eab4e1df8f",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"3": {
"node_id": "54c6a119-d914-4690-aa3c-1275d55efe5a",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {},
"hash": "06d6c13287ff7e2f033a1aae487198dbfdec3d954aab0fd9b4866ce833200afb",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
}
},
"text": "AGI 课堂推出的社群型会员制课程,传授大模型的原理、应用开发技术和行业认知,助你成为 ChatGPT 浪潮中的超级个体\n什么是 AI",
"mimetype": "text/plain",
"start_char_idx": 33,
"end_char_idx": 100,
"text_template": "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}",
"metadata_template": "{key}: {value}",
"metadata_seperator": "\n",
"class_name": "TextNode"
}
LlamaIndex 提供了丰富的 TextSplitter,例如:
SentenceSplitter:在切分指定长度的 chunk 同时尽量保证句子边界不被切断;CodeSplitter:根据 AST(编译器的抽象句法树)切分代码,保证代码功能片段完整;SemanticSplitterNodeParser:根据语义相关性对将文本切分为片段。
4.2、使用 NodeParsers 对有结构的文档做解析
例如:MarkdownNodeParser解析 markdown 文档
1 | from llama_index.readers.file import FlatReader |
1 | show_json(nodes[2].json()) |
{
"id_": "5c2eb25f-08ac-4b2e-9050-bc6efa90304a",
"embedding": null,
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md",
"Header_2": "功能"
},
"excluded_embed_metadata_keys": [],
"excluded_llm_metadata_keys": [],
"relationships": {
"1": {
"node_id": "f3be7692-141b-41a6-8b3f-58402aaf36c1",
"node_type": "4",
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md"
},
"hash": "45b9149e0039c1ef7fbbd74f96923875505cc77916de48734ba7767f6a16a87e",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"2": {
"node_id": "3722d2c3-6638-453c-8fe1-f2af97fc8452",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md",
"Header_2": "屏幕截图"
},
"hash": "f6065ad5e9929bc7ee14e3c4cc2d29c06788501df8887476c30b279ba8ffd594",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"3": {
"node_id": "c5dcf1d3-7a6a-48b0-b6d8-06457b182ac5",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {
"Header_2": "功能",
"Header_3": "这是你吗?"
},
"hash": "f54ac07d417fbcbd606e7cdd3de28c30804e2213218dec2e6157d5037a23e289",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
}
},
"text": "功能\n\n基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的 AI 机器人非常神奇。然而,它们的行为可能是随机的,不同的机器人在不同的任务上表现也有差异。如果你想获得最佳体验,不要一个一个尝试。ChatALL(中文名:齐叨)可以把一条指令同时发给多个 AI,帮助您发现最好的回答。你需要做的只是[下载、安装](https://github.com/sunner/ChatALL/releases)和提问。",
"mimetype": "text/plain",
"start_char_idx": 459,
"end_char_idx": 650,
"text_template": "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}",
"metadata_template": "{key}: {value}",
"metadata_seperator": "\n",
"class_name": "TextNode"
}
{
"id_": "c5dcf1d3-7a6a-48b0-b6d8-06457b182ac5",
"embedding": null,
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md",
"Header_2": "功能",
"Header_3": "这是你吗?"
},
"excluded_embed_metadata_keys": [],
"excluded_llm_metadata_keys": [],
"relationships": {
"1": {
"node_id": "f3be7692-141b-41a6-8b3f-58402aaf36c1",
"node_type": "4",
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md"
},
"hash": "45b9149e0039c1ef7fbbd74f96923875505cc77916de48734ba7767f6a16a87e",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"2": {
"node_id": "5c2eb25f-08ac-4b2e-9050-bc6efa90304a",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {
"filename": "ChatALL.md",
"extension": ".md",
"Header_2": "功能"
},
"hash": "90172566aa1795d0f9ac33c954d0b98fde63bf9176950d0ea38e87e4ab6563ed",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
},
"3": {
"node_id": "7d959c37-6ff9-4bfe-b499-c509a24088cb",
"node_type": "1",
"metadata": {
"Header_2": "功能",
"Header_3": "支持的 AI"
},
"hash": "1b2b11abec9fc74b725b6c344f37d44736e8e991a3eebdbcfa4ab682506c7b2e",
"class_name": "RelatedNodeInfo"
}
},
"text": "这是你吗?\n\nChatALL 的典型用户是:\n\n- 🤠**大模型重度玩家**,希望从大模型找到最好的答案,或者最好的创作\n- 🤓**大模型研究者**,直观比较各种大模型在不同领域的优劣\n- 😎**大模型应用开发者**,快速调试 prompt,寻找表现最佳的基础模型",
"mimetype": "text/plain",
"start_char_idx": 656,
"end_char_idx": 788,
"text_template": "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}",
"metadata_template": "{key}: {value}",
"metadata_seperator": "\n",
"class_name": "TextNode"
}
更多的 NodeParser 包括 HTMLNodeParser,JSONNodeParser等等。
5、索引(Indexing)与检索(Retrieval)
基础概念:在「检索」相关的上下文中,「索引」即index, 通常是指为了实现快速检索而设计的特定「数据结构」。
索引的具体原理与实现不是本课程的教学重点,感兴趣的同学可以参考:传统索引、向量索引
5.1、向量检索
SimpleVectorStore直接在内存中构建一个 Vector Store 并建索引
1 | from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader |
an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly available data. We also
increased the size of the pretraining corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and
adopted grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of Llama 2 with
7B, 13B, and 70B parameters. We have also trained 34B variants, which we report on in this paper
but are not releasing.§
2. Llama 2-Chat, a fine-tuned version of Llama 2 that is optimized for dialogue use cases. We release
variants of this model with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters as well.
We believe that the open release of LLMs, when done safely, will be a net benefit to society. Like all LLMs,
Llama 2 is a new technology that carries potential risks with use (Bender et al., 2021b; Weidinger et al., 2021;
Solaiman et al., 2023). Testing conducted to date has been in English and has not — and could not — cover
all scenarios. Therefore, before deploying any applications of
Koura Marie-Anne Lachaux Thibaut Lavril Jenya Lee Diana Liskovich
Yinghai Lu Yuning Mao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov Pushkar Mishra
Igor Molybog Yixin Nie Andrew Poulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi Rungta Kalyan Saladi
Alan Schelten Ruan Silva Eric Michael Smith Ranjan Subramanian Xiaoqing Ellen Tan Binh Tang
Ross Taylor Adina Williams Jian Xiang Kuan Puxin Xu Zheng Yan Iliyan Zarov Yuchen Zhang
Angela Fan Melanie Kambadur Sharan Narang Aurelien Rodriguez Robert Stojnic
Sergey Edunov
Thomas Scialom∗
GenAI, Meta
Abstract
In this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a collection of pretrained and fine-tuned
large language models (LLMs) ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
Our fine-tuned LLMs, called Llama 2-Chat, are optimized for dialogue use cases. Our
models outperform open-source chat models on most benchmarks we tested, and based on
our human evaluations for helpfulness and safety, may be a suitable substitute for
LlamaIndex 默认的 Embedding 模型是 OpenAIEmbedding(model="text-embedding-ada-002")。
如何替换指定的 Embedding 模型见后面章节详解。
- 使用自定义的 Vector Store,以
Qdrant为例:
1 | !pip install llama-index-vector-stores-qdrant |
1 | from llama_index.core.indices.vector_store.base import VectorStoreIndex |
Node ID: bd3ff0be-13b9-4f7c-bac3-71ef38978766
Text: an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly
available data. We also increased the size of the pretraining corpus
by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and adopted grouped-
query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of
Llama 2 with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters. We have also trained 34B
variants,...
Score: 0.790
Node ID: 18282125-5744-4da8-afe6-32b208304571
Text: Koura Marie-Anne Lachaux Thibaut Lavril Jenya Lee Diana
Liskovich Yinghai Lu Yuning Mao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov Pushkar
Mishra Igor Molybog Yixin Nie Andrew Poulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi
Rungta Kalyan Saladi Alan Schelten Ruan Silva Eric Michael Smith
Ranjan Subramanian Xiaoqing Ellen Tan Binh Tang Ross Taylor Adina
Williams Jian Xiang...
Score: 0.789
5.2、更多索引与检索方式
LlamaIndex 内置了丰富的检索机制,例如:
关键字检索
BM25Retriever:基于 tokenizer 实现的 BM25 经典检索算法KeywordTableGPTRetriever:使用 GPT 提取检索关键字KeywordTableSimpleRetriever:使用正则表达式提取检索关键字KeywordTableRAKERetriever:使用RAKE算法提取检索关键字(有语言限制)
RAG-Fusion
QueryFusionRetriever还支持 KnowledgeGraph、SQL、Text-to-SQL 等等
5.3、Ingestion Pipeline 自定义数据处理流程
LlamaIndex 通过 Transformations 定义一个数据(Documents)的多步处理的流程(Pipeline)。
这个 Pipeline 的一个显著特点是,它的每个子步骤是可以缓存(cache)的,即如果该子步骤的输入与处理方法不变,重复调用时会直接从缓存中获取结果,而无需重新执行该子步骤,这样即节省时间也会节省 token (如果子步骤涉及大模型调用)。
1 | import time |
1 | from llama_index.core.indices.vector_store.base import VectorStoreIndex |
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:01<00:00, 2.99it/s]
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 5.62it/s]
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:00<00:00, 5.85it/s]
100%|██████████| 4/4 [00:02<00:00, 1.68it/s]
耗时 8875.431299209595 ms
Node ID: b48b5c44-9287-4056-bdae-f8dc1393d44d
Text: Llama 2, an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of
publicly available data. We also increased the size of the pretraining
corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and adopted
grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing
variants of Llama 2 with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters. We have also
trained 34B ...
Score: 0.783
本地保存 IngestionPipeline 的缓存
1 | pipeline.persist("./pipeline_storage") |
1 | new_pipeline = IngestionPipeline( |
耗时 3.515005111694336 ms
此外,也可以用远程的 Redis 或 MongoDB 等存储 IngestionPipeline 的缓存,具体参考官方文档:Remote Cache Management。
IngestionPipeline 也支持异步和并发调用,请参考官方文档:Async Support、Parallel Processing。
5.4、检索后处理
LlamaIndex 的 Node Postprocessors 提供了一系列检索后处理模块。
例如:我们可以用不同模型对检索后的 Nodes 做重排序
1 | # 获取 retriever |
[0] Llama 2, an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly available data. We also
increased the size of the pretraining corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and
adopted grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of Llama 2 with
7B, 13B, and 70B parameters. We have also trained 34B variants, which we report on in this paper
but are not releasing.§
2. Llama 2-Chat, a fine-tuned version of Llama 2 that is optimized for dialogue use cases. We release
variants of this model with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters as well.
We believe that the open release of LLMs, when done safely, will be a net benefit to society. Like all LLMs,
Llama 2 is a new technology that carries potential risks with use (Bender et al., 2021b; Weidinger et al., 2021;
Solaiman et al., 2023).
[1] We release
variants of this model with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters as well.
We believe that the open release of LLMs, when done safely, will be a net benefit to society. Like all LLMs,
Llama 2 is a new technology that carries potential risks with use (Bender et al., 2021b; Weidinger et al., 2021;
Solaiman et al., 2023). Testing conducted to date has been in English and has not — and could not — cover
all scenarios. Therefore, before deploying any applications of Llama 2-Chat, developers should perform
safety testing and tuning tailored to their specific applications of the model. We provide a responsible use
guide¶ and code examples‖ to facilitate the safe deployment of Llama 2 and Llama 2-Chat. More details of
our responsible release strategy can be found in Section 5.3.
[2] Marie-Anne Lachaux Thibaut Lavril Jenya Lee Diana Liskovich
Yinghai Lu Yuning Mao Xavier Martinet Todor Mihaylov Pushkar Mishra
Igor Molybog Yixin Nie Andrew Poulton Jeremy Reizenstein Rashi Rungta Kalyan Saladi
Alan Schelten Ruan Silva Eric Michael Smith Ranjan Subramanian Xiaoqing Ellen Tan Binh Tang
Ross Taylor Adina Williams Jian Xiang Kuan Puxin Xu Zheng Yan Iliyan Zarov Yuchen Zhang
Angela Fan Melanie Kambadur Sharan Narang Aurelien Rodriguez Robert Stojnic
Sergey Edunov
Thomas Scialom∗
GenAI, Meta
Abstract
In this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a collection of pretrained and fine-tuned
large language models (LLMs) ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
Our fine-tuned LLMs, called Llama 2-Chat, are optimized for dialogue use cases.
[3] These closed product LLMs are heavily fine-tuned to align with human
preferences, which greatly enhances their usability and safety. This step can require significant costs in
compute and human annotation, and is often not transparent or easily reproducible, limiting progress within
the community to advance AI alignment research.
In this work, we develop and release Llama 2, a family of pretrained and fine-tuned LLMs, Llama 2 and
Llama 2-Chat, at scales up to 70B parameters. On the series of helpfulness and safety benchmarks we tested,
Llama 2-Chat models generally perform better than existing open-source models. They also appear to
be on par with some of the closed-source models, at least on the human evaluations we performed (see
Figures 1 and 3). We have taken measures to increase the safety of these models, using safety-specific data
annotation and tuning, as well as conducting red-teaming and employing iterative evaluations. Additionally,
this paper contributes a thorough description of our fine-tuning methodology and approach to improving
LLM safety.
[4] Figure 3: Safety human evaluation results for Llama 2-Chat compared to other open-source and closed-
source models. Human raters judged model generations for safety violations across ~2,000 adversarial
prompts consisting of both single and multi-turn prompts. More details can be found in Section 4.4. It is
important to caveat these safety results with the inherent bias of LLM evaluations due to limitations of the
prompt set, subjectivity of the review guidelines, and subjectivity of individual raters. Additionally, these
safety evaluations are performed using content standards that are likely to be biased towards the Llama
2-Chat models.
We are releasing the following models to the general public for research and commercial use‡:
1. Llama 2, an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly available data. We also
increased the size of the pretraining corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and
adopted grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of Llama 2 with
7B, 13B, and 70B parameters.
1 | from llama_index.core.postprocessor import SentenceTransformerRerank |
/opt/conda/lib/python3.11/site-packages/tqdm/auto.py:21: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
/home/jovyan/.local/lib/python3.11/site-packages/huggingface_hub/file_download.py:1132: FutureWarning: `resume_download` is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0. Downloads always resume when possible. If you want to force a new download, use `force_download=True`.
warnings.warn(
[0] Figure 3: Safety human evaluation results for Llama 2-Chat compared to other open-source and closed-
source models. Human raters judged model generations for safety violations across ~2,000 adversarial
prompts consisting of both single and multi-turn prompts. More details can be found in Section 4.4. It is
important to caveat these safety results with the inherent bias of LLM evaluations due to limitations of the
prompt set, subjectivity of the review guidelines, and subjectivity of individual raters. Additionally, these
safety evaluations are performed using content standards that are likely to be biased towards the Llama
2-Chat models.
We are releasing the following models to the general public for research and commercial use‡:
1. Llama 2, an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly available data. We also
increased the size of the pretraining corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and
adopted grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of Llama 2 with
7B, 13B, and 70B parameters.
[1] Llama 2, an updated version of Llama 1, trained on a new mix of publicly available data. We also
increased the size of the pretraining corpus by 40%, doubled the context length of the model, and
adopted grouped-query attention (Ainslie et al., 2023). We are releasing variants of Llama 2 with
7B, 13B, and 70B parameters. We have also trained 34B variants, which we report on in this paper
but are not releasing.§
2. Llama 2-Chat, a fine-tuned version of Llama 2 that is optimized for dialogue use cases. We release
variants of this model with 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters as well.
We believe that the open release of LLMs, when done safely, will be a net benefit to society. Like all LLMs,
Llama 2 is a new technology that carries potential risks with use (Bender et al., 2021b; Weidinger et al., 2021;
Solaiman et al., 2023).
更多的 Rerank 及其它后处理方法,参考官方文档:Node Postprocessor Modules
6、生成回复(QA & Chat)
6.1、单轮问答(Query Engine)
1 | qa_engine = index.as_query_engine() |
Llama 2有7B, 13B, 和70B参数。
流式输出
1 | qa_engine = index.as_query_engine(streaming=True) |
Llama 2有7B, 13B, 和70B参数。
6.2、多轮对话(Chat Engine)
1 | chat_engine = index.as_chat_engine() |
Llama2 有7B, 13B, 和70B参数。
1 | response = chat_engine.chat("How many at most?") |
Llama2 最多有70B参数。
流式输出
1 | chat_engine = index.as_chat_engine() |
Llama 2有7B、13B和70B参数变体。
7、底层接口:Prompt、LLM 与 Embedding
7.1、Prompt 模板
PromptTemplate 定义提示词模板
1 | from llama_index.core import PromptTemplate |
'写一个关于小明的笑话'
ChatPromptTemplate 定义多轮消息模板
1 | from llama_index.core.llms import ChatMessage, MessageRole |
system: 你叫瓜瓜,你必须根据用户提供的上下文回答问题。
user: 已知上下文:
这是一个测试
问题:这是什么
assistant:
7.2、语言模型
1 | from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI |
1 | response = llm.complete(prompt.format(topic="小明")) |
小明有一天去参加一个智力竞赛,主持人问他:“小明,请用‘因为’和‘所以’造一个句子。”
小明想了想,说:“因为今天我没带作业,所以我来参加比赛了。”
1 | response = llm.complete( |
我是瓜瓜,你的智能助手。根据你提供的上下文,我们正在进行一个测试。请让我知道如果你有其他问题或需要进一步的帮助!
设置全局使用的语言模型
1 | from llama_index.core import Settings |
除 OpenAI 外,LlamaIndex 已集成多个大语言模型,包括云服务 API 和本地部署 API,详见官方文档:Available LLM integrations
7.3、Embedding 模型
1 | from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding |
LlamaIndex 同样集成了多种 Embedding 模型,包括云服务 API 和开源模型(HuggingFace)等,详见官方文档。
8、基于 LlamaIndex 实现一个功能较完整的 RAG 系统
功能要求:
- 加载指定目录的文件
- 支持 RAG-Fusion
- 使用 Qdrant 向量数据库,并持久化到本地
- 支持检索后排序
- 支持多轮对话
1 | from qdrant_client import QdrantClient |
1 | from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, KeywordTableIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader |
1 | while True: |
User: llama2有多少参数
AI: Llama 2 有 7B、13B 和 70B 参数的变体。
User: 最多多少
AI: Llama 2 的变体中参数最多的是 70B。
6、LLamaIndex简介






